Tropical regions are considered to be the regions around the Equator. Above and below the Equator (0 degrees) to 23.27 degrees North (Tropic of Cancer) and South (Tropic of Capricon). Up to 35 degrees is approximately a subtropical zone.
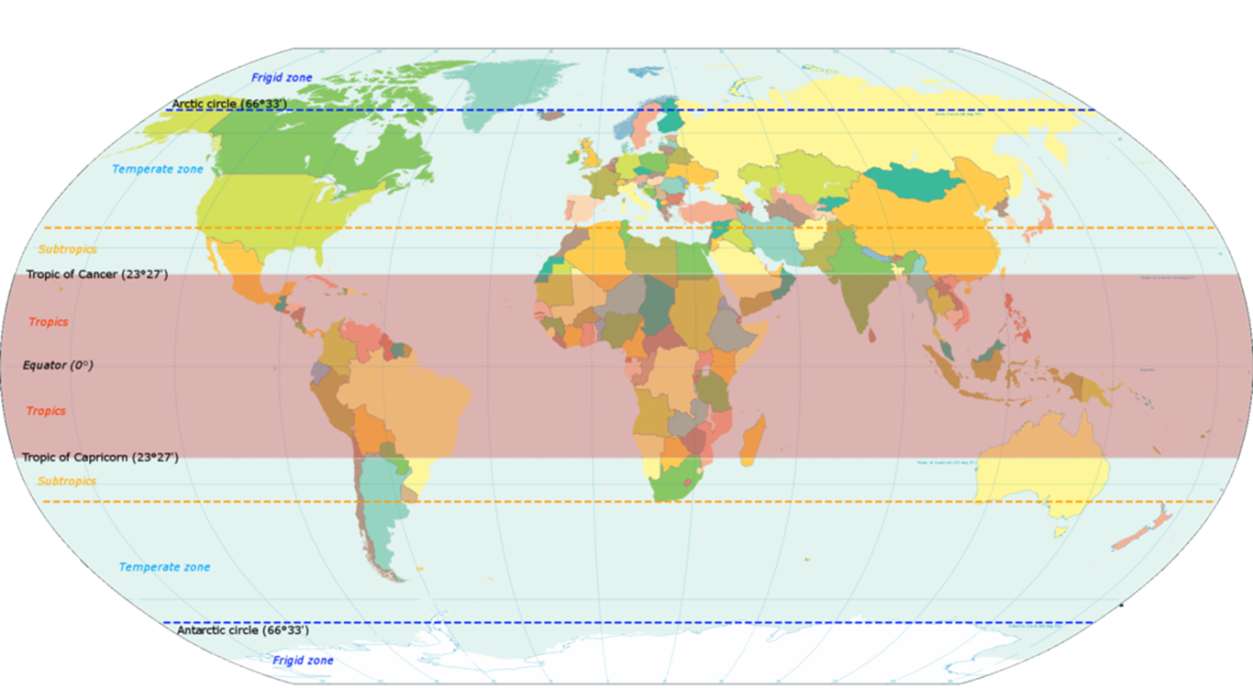
Tropical regions make up 40% of the Earth’s region, vast amounts of water and land. The tropical climate is similar through the whole year, with many places having rainy/wet and dry periods. That is why there is a huge source of fresh air and water that is of great importance to humanity and the planet.
Unfortunately, major problems are plaguing regions affecting countries in the islands, atolls in the Caribbean, Indian Ocean, Asian and Pacific. Problems such as major nuclear testing, massive destruction of greenery, soil, coral destruction and over-fishing have caused damage in these parts, which spills over into other parts of the world.
Colonialist countries such as England, France, Spain, America in the past began the colonization and enslavement of humans and the surrounding areas (including wildlife) because they saw great potential in islands and atolls.
All this combined alongside with other factors, are creating great issues in modern times to the islands in the tropics and subtropics worldwide.

